
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Brain_lobes-571a4c0f5f9b58857db90d7e.jpg)
The inferior parietal lobe also contains the supramarginal gyrus, which sits around the posterior end of the Sylvian fissure. The inferior region of the parietal lobe, close to the Sylvian fissure, houses the gustatory cortex where information about taste is processed. The superior parietal lobe is associated with proprioception (where the body is oriented in space), attention (particularly spatial attention), spatial reasoning and mathematical ability. The primary somatosensory cortex is behind the central sulcus, and it receives information from the body about touch, temperature and pain.
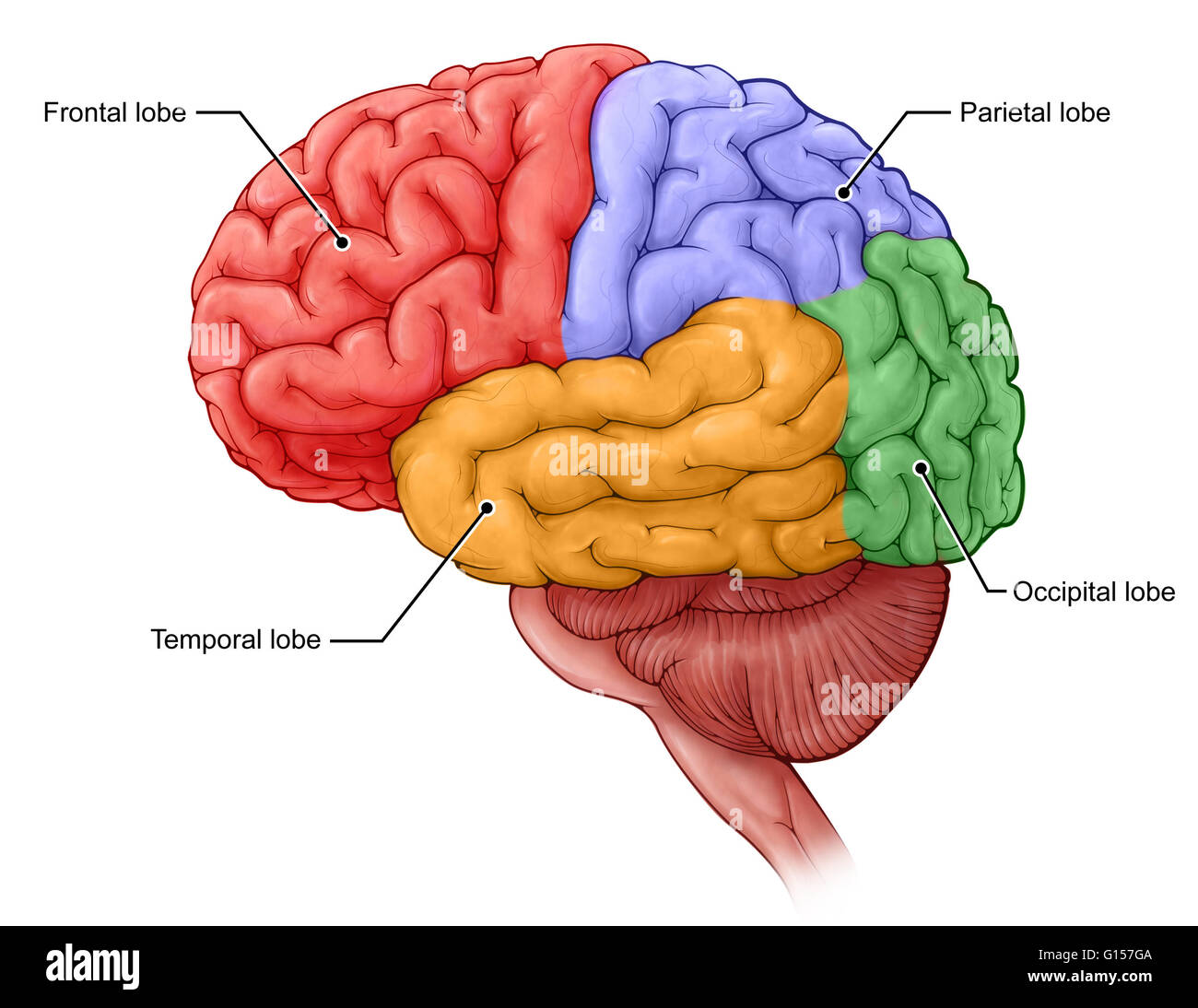
The cognitive functions associated with these lobes can be summarized as follows: The main part of the brain is called the cerebral cortex, and it is divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). The brain creates, stores and retrieves memories, as well as controlling body movements to enable action and communication.

The brain receives information from sensory inputs and uses that information to make sense of the world, by comparing and integrating it with past experiences. It is responsible for everything that we do, feel and perceive. The human brain is the centre of the body’s nervous system and the seat of cognition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
